Here are the pictures from our climb up the wonderful Kirkstone Pass during our adventure. Ten kilometres up to an altitude of 1,489 feet (454 metres), with a pleasant average gradient of around 4 per cent, but tougher sections at 12-13 per cent.
This is the longest route up the climb, but there’s always ‘The Struggle’ for those of you who fancy a tougher challenge. Gradients up to 25 per cent will definitely leave you feeling like you’ve earned a drink when you reach the Kirkstone Pass Inn at the top!
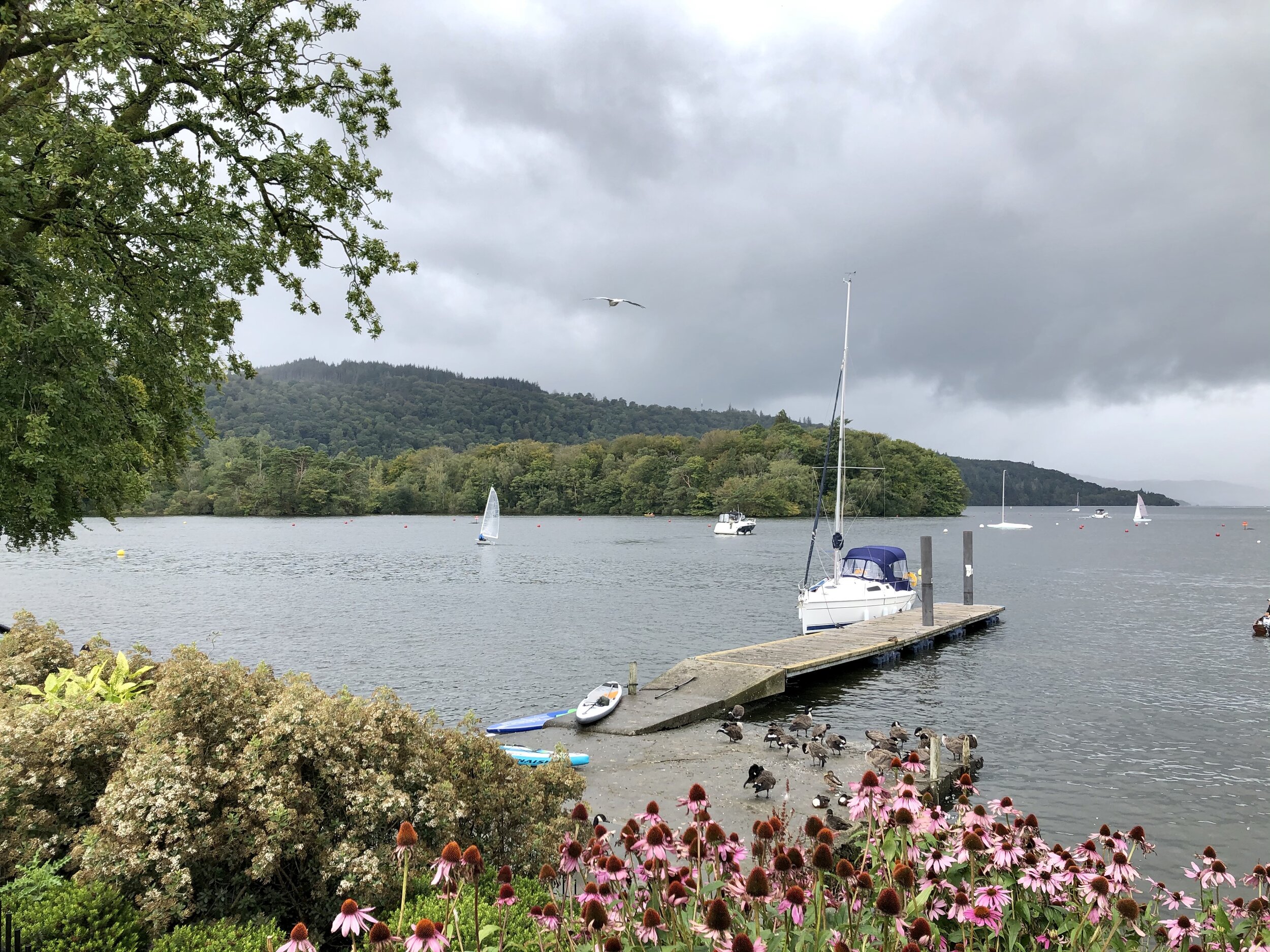

Lunch by the lake before we take on the famous climb.
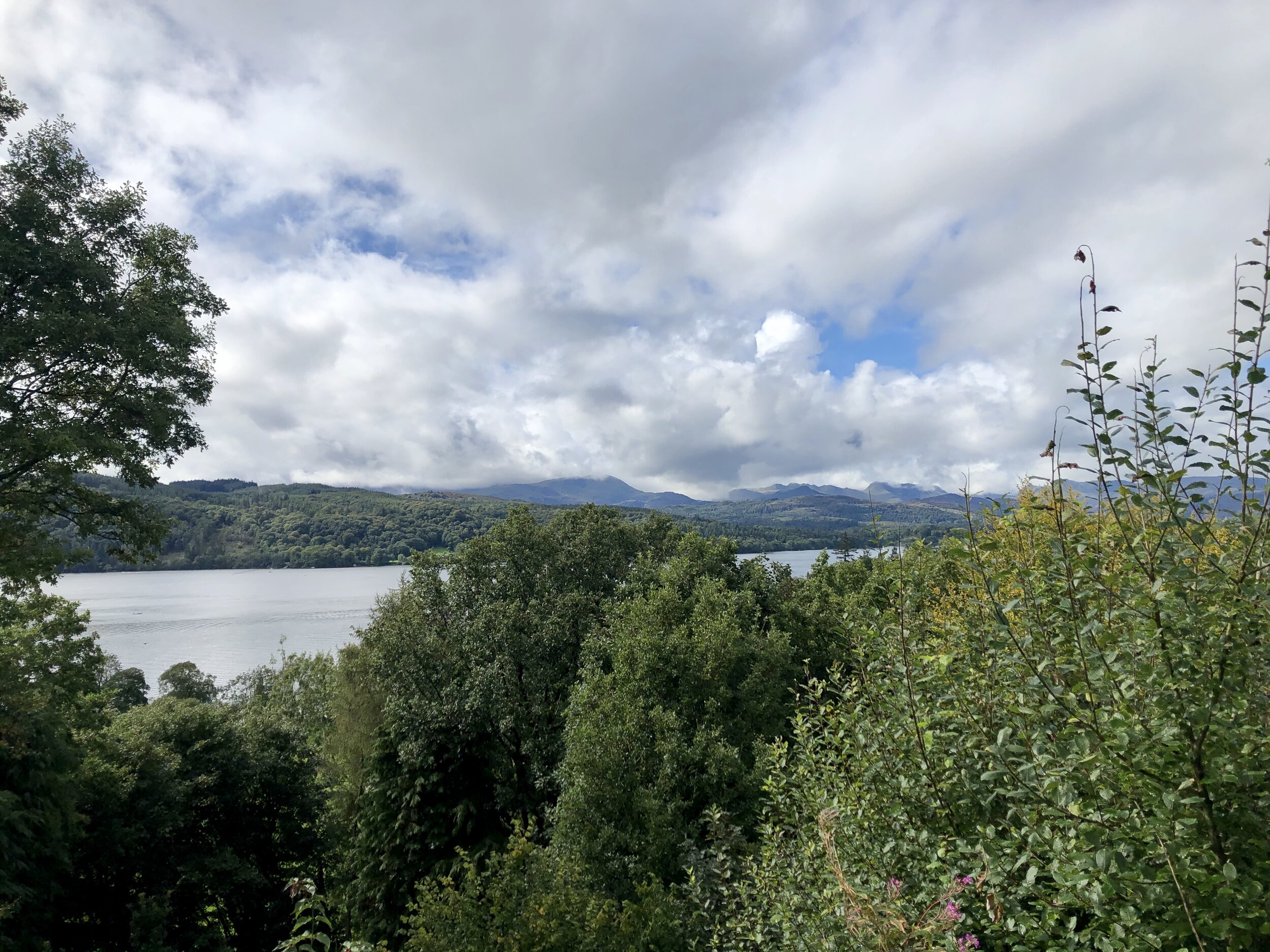

Our last views of Windermere. Next stop Ullswater.
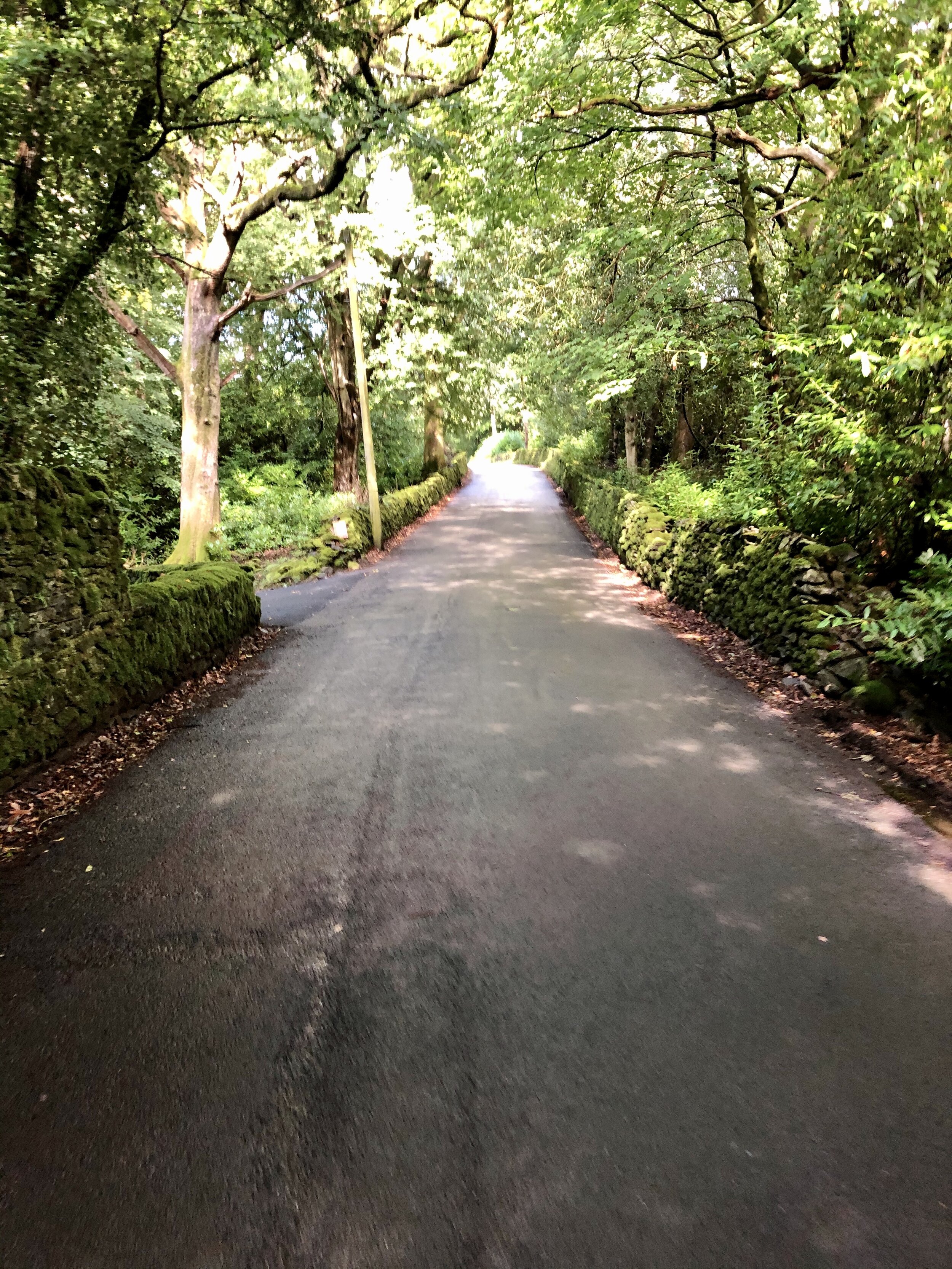

The B-road from Troutbeck Bridge immediately kicks up through the trees .
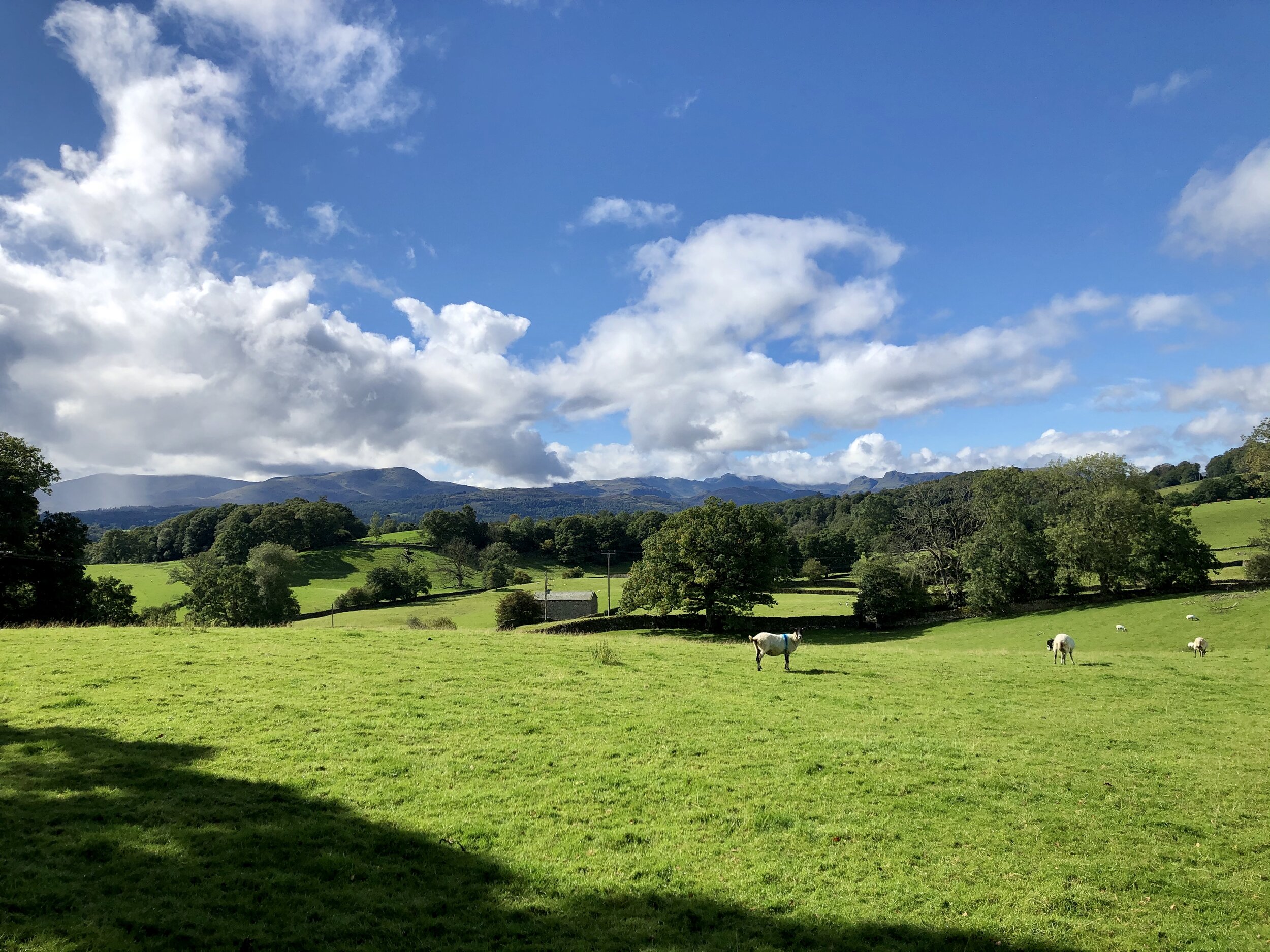

But the climb is instantly worth it for the views.
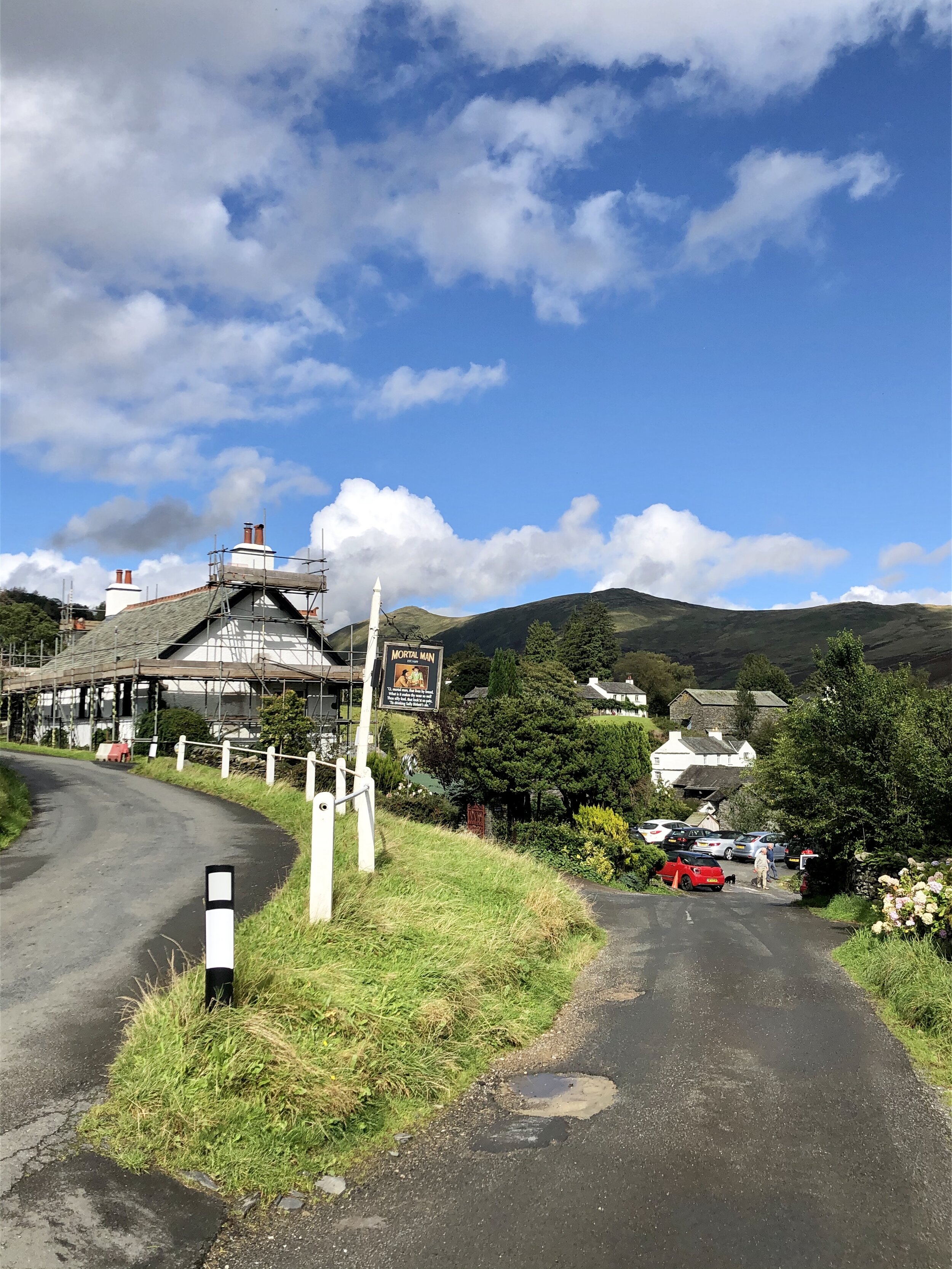

We pass through some beautiful old villages, full of white painted stone cottages and quaint little pubs.
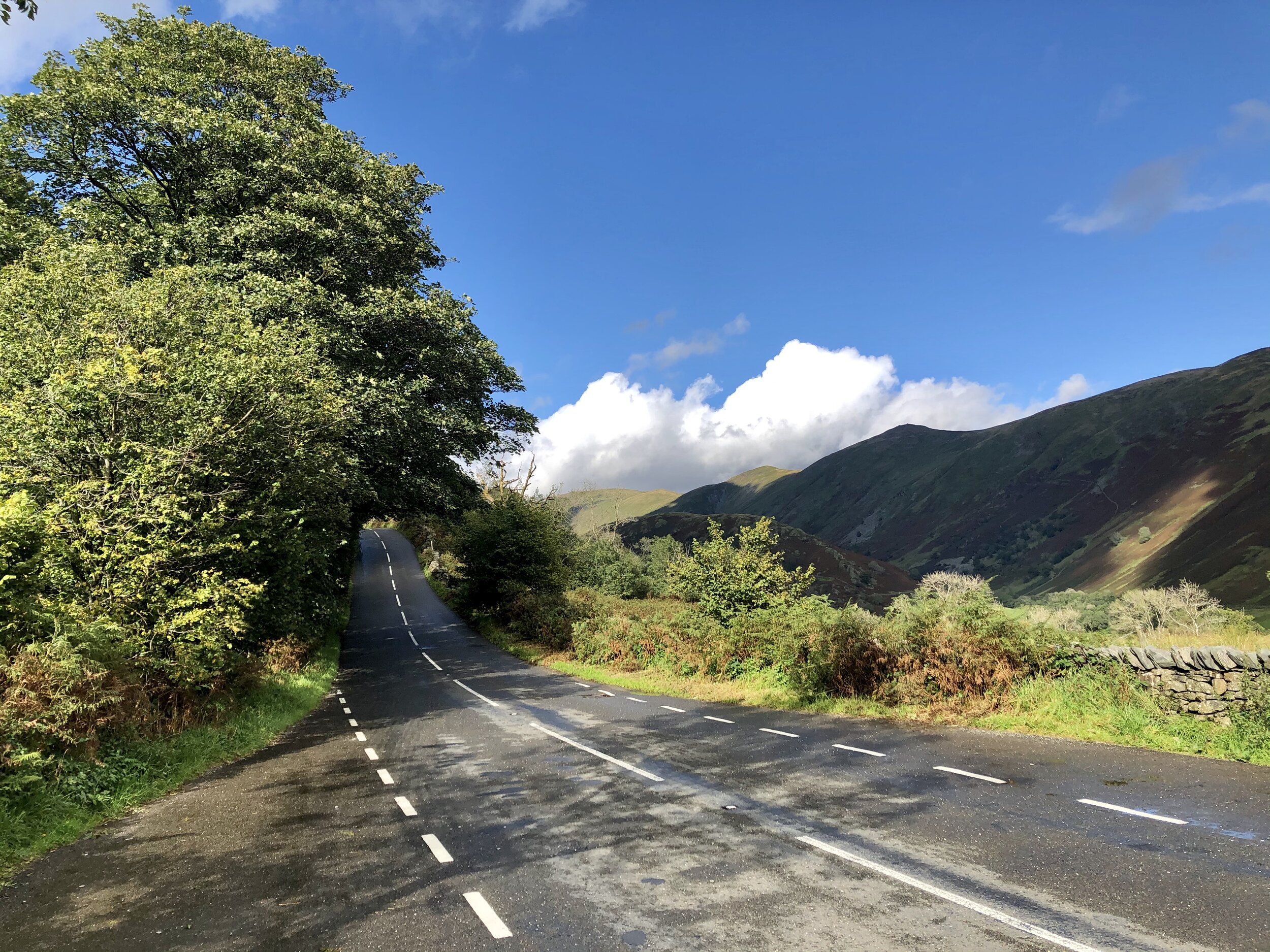

And the gradient kicks again.
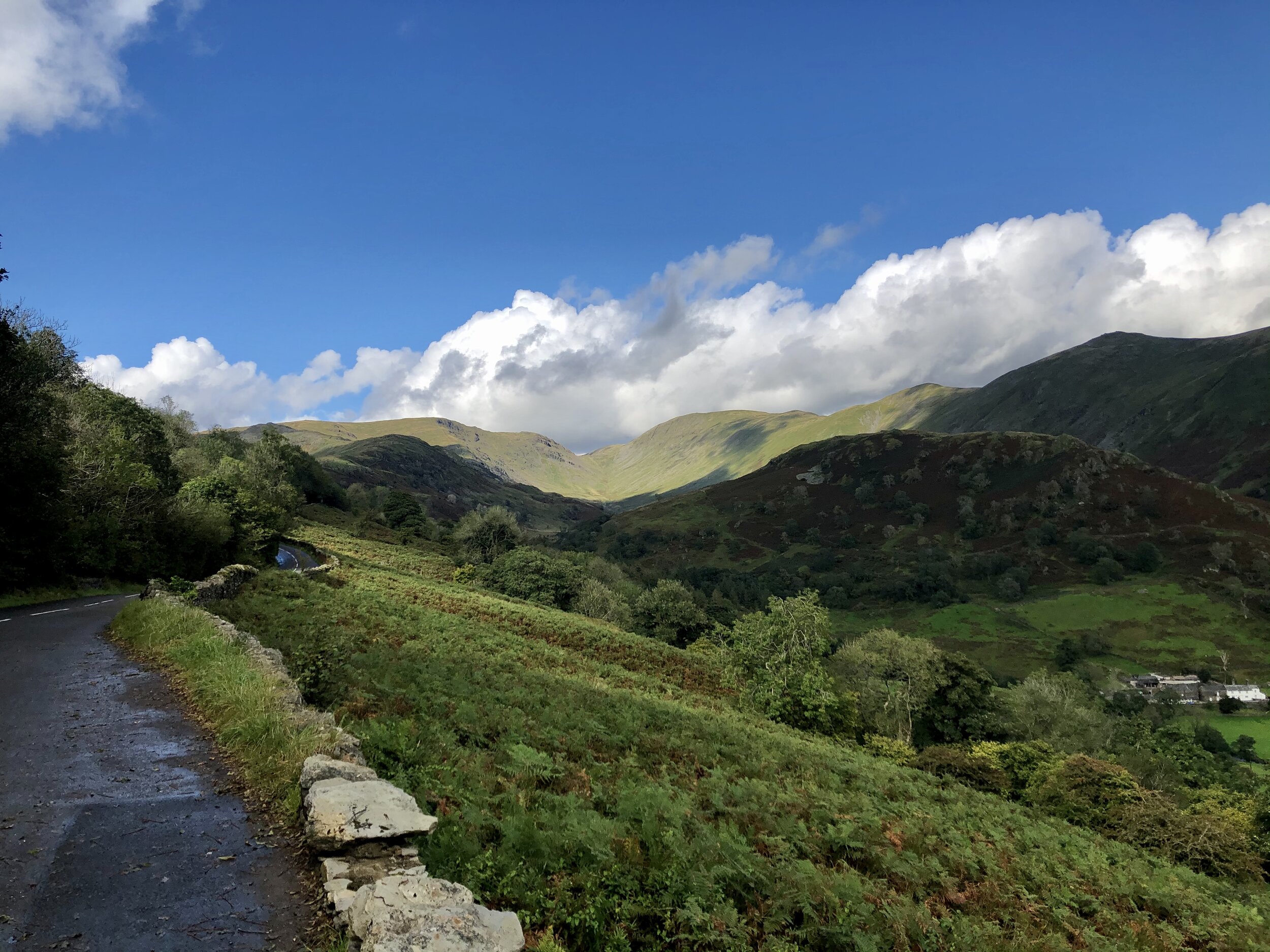

England’s green and pleasant (if rather hilly) land.
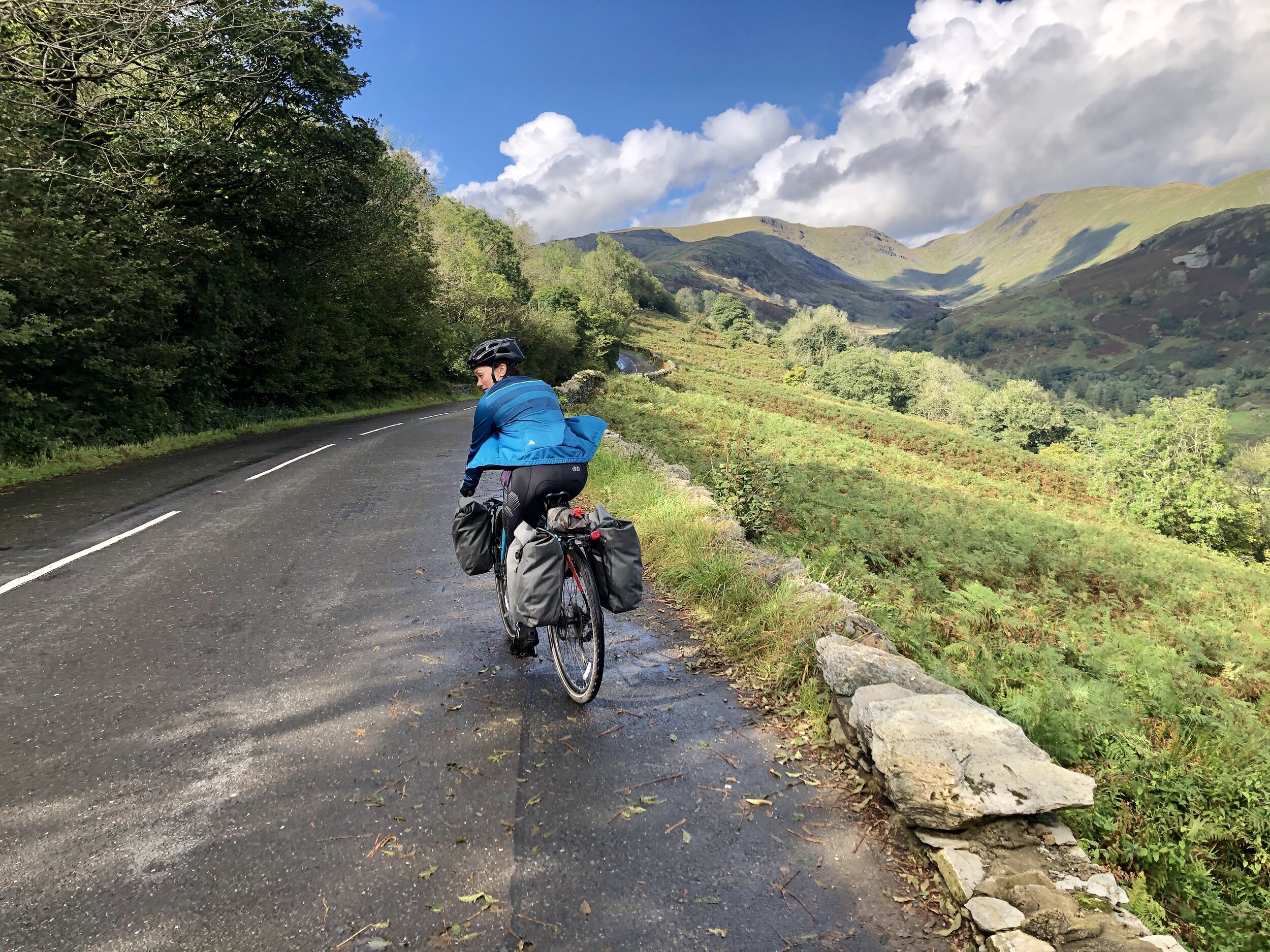

Lou powering up the road after a quick photo stop.
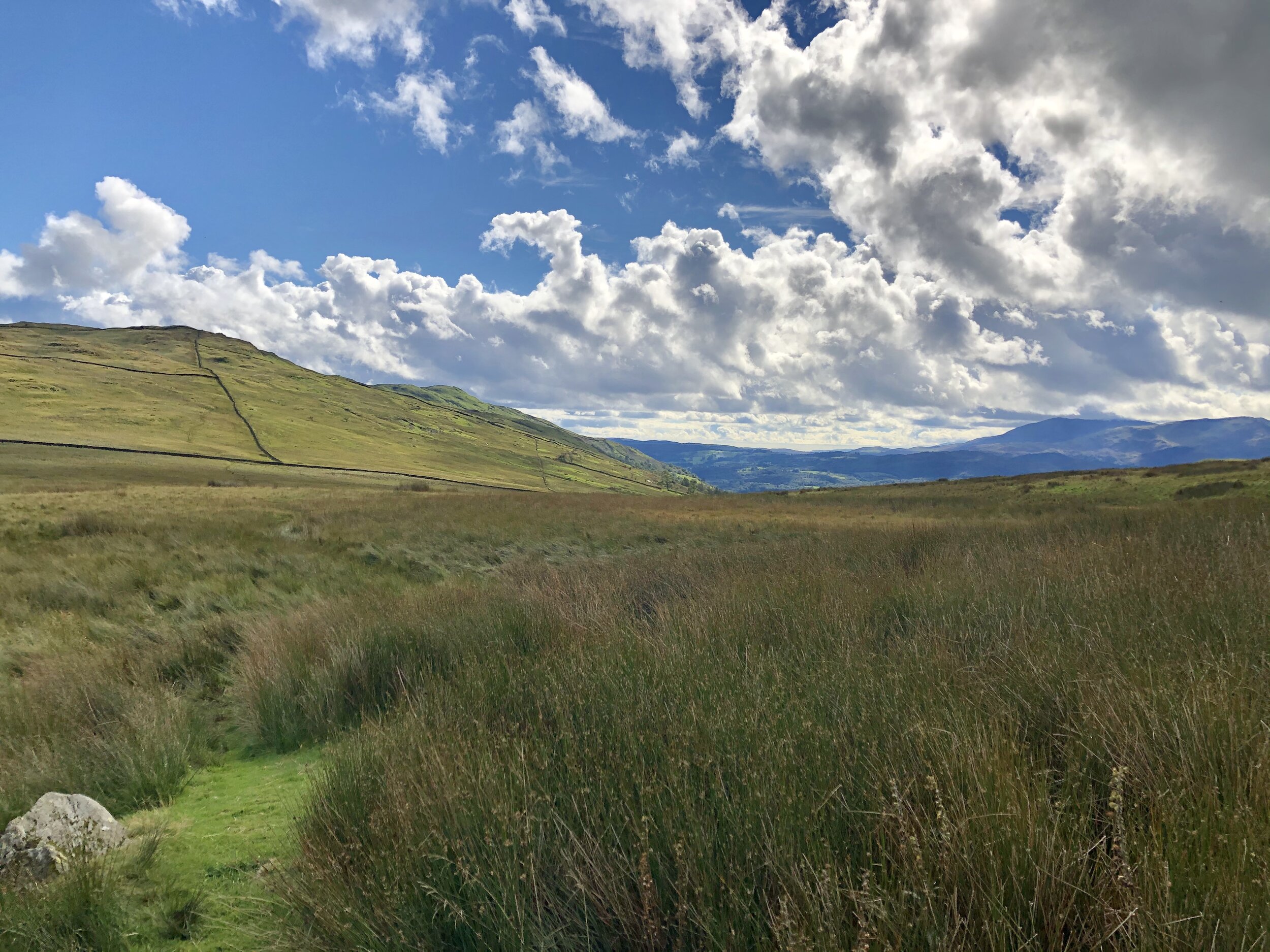

Well, not quite, but the views stretch for miles.
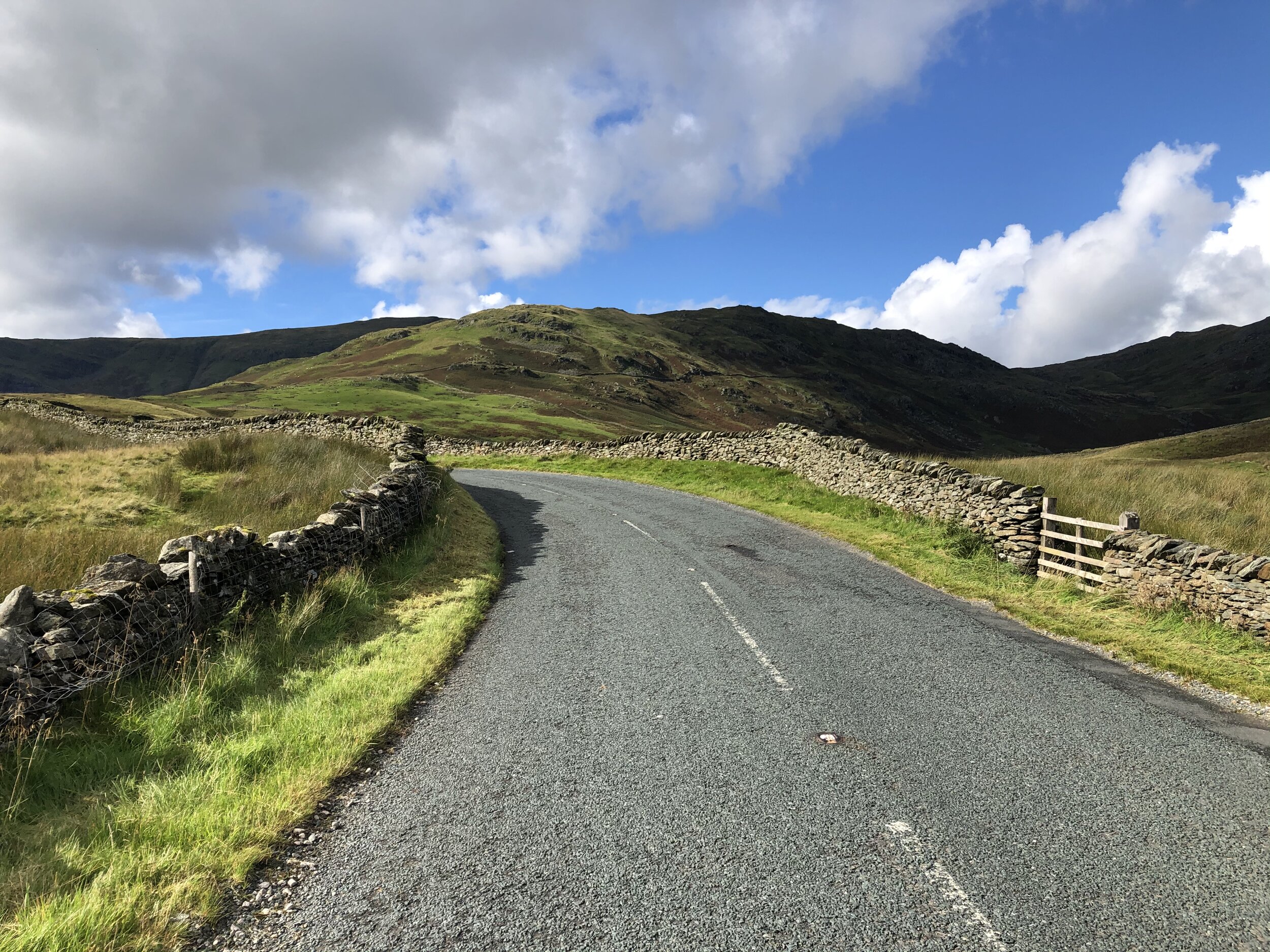

The gradient relents, but still we climb.
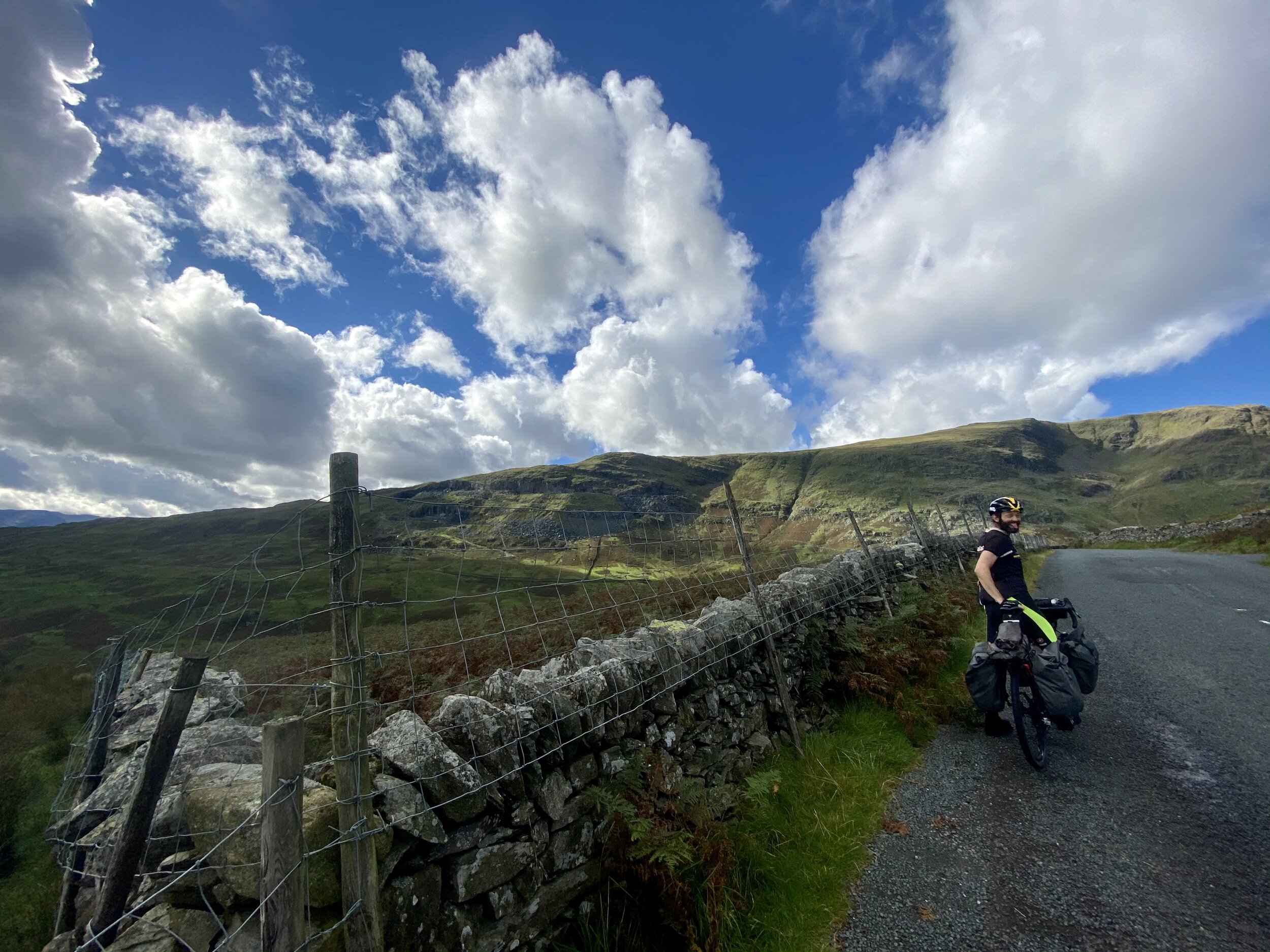

Me proving I cycled up too and didn’t just sit in a car taking photos.
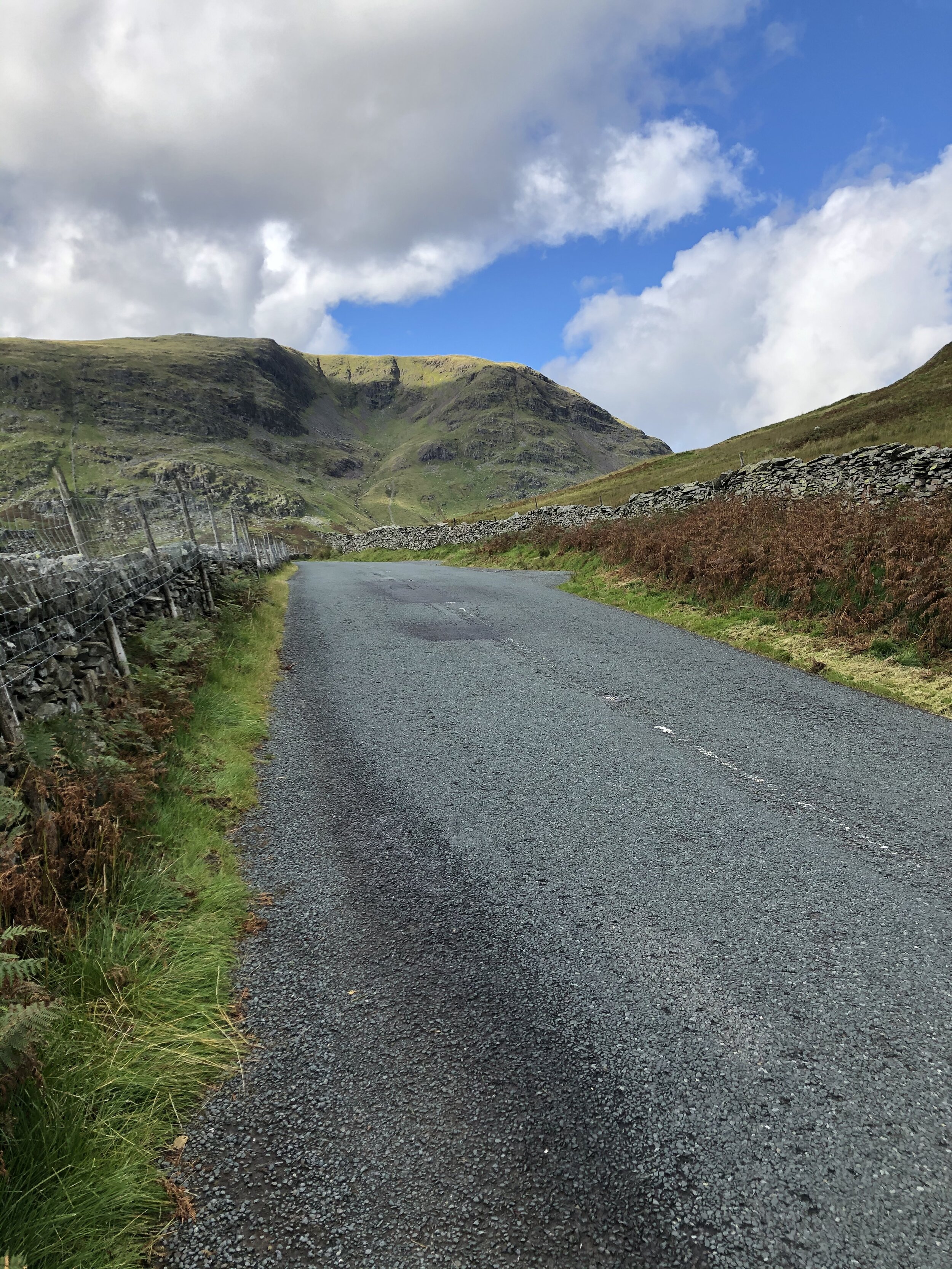

The road kicks once more.
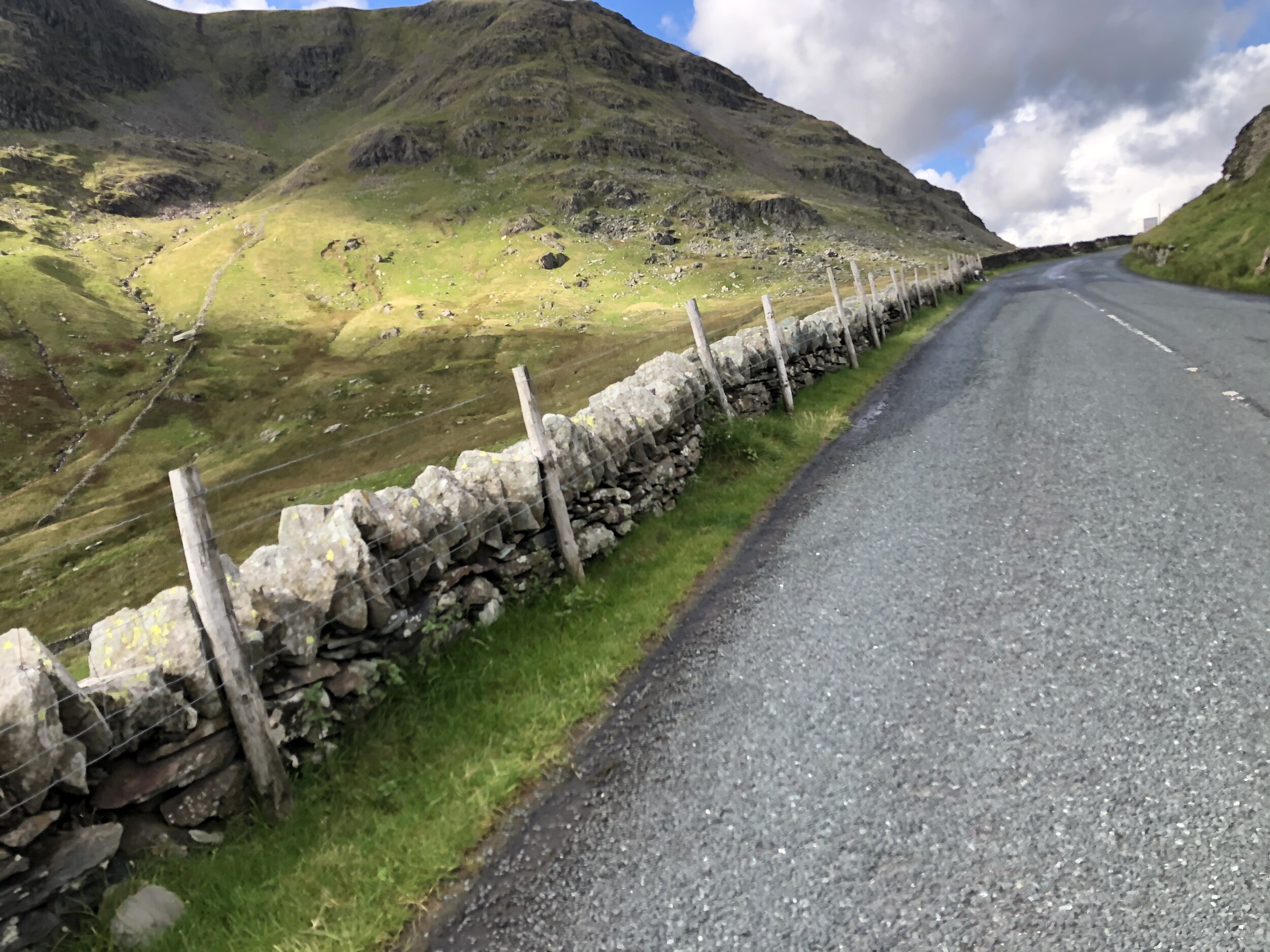

Ok, maybe twice more.
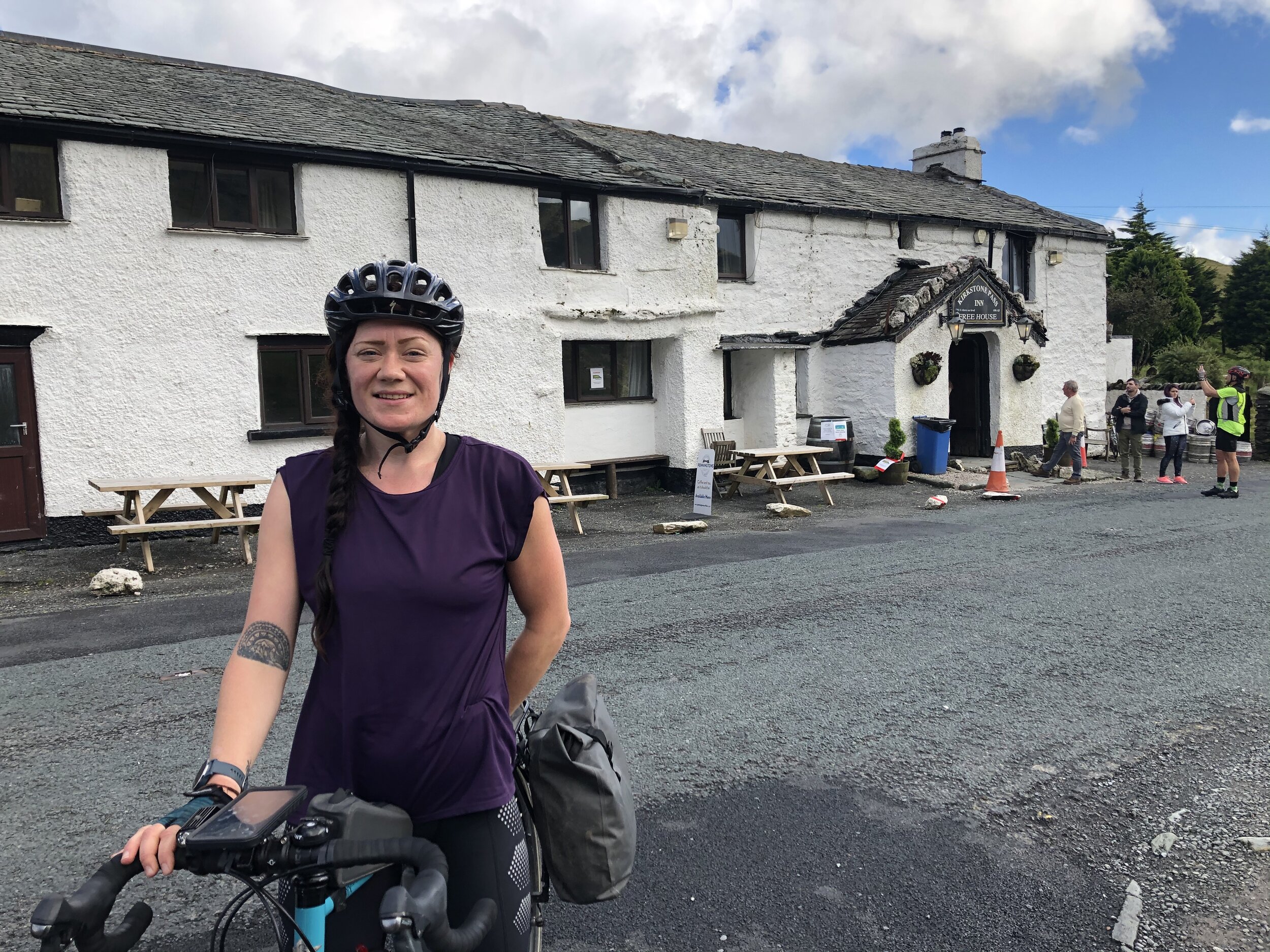

Lou pauses for a photo in front of the famous Kirkstone Pass Inn.

A very kind cyclist offers to buy us both a drink, thinking we’re taking on the same challenge as him. We’re not allowed inside the pub of course (due to COVID), but at least the sun is shining.
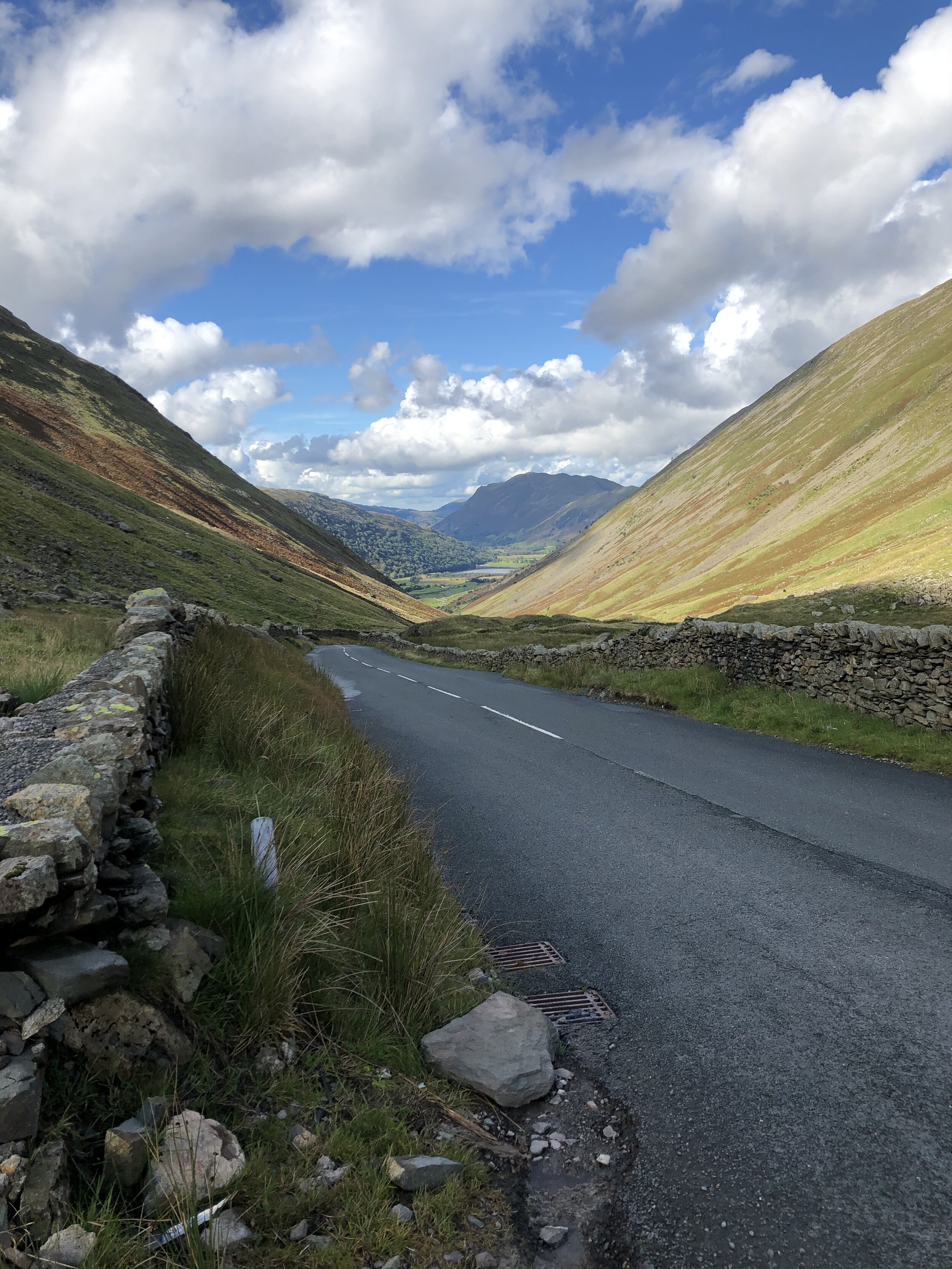

The view over the other side. Downhill all the way to Ullswater now.
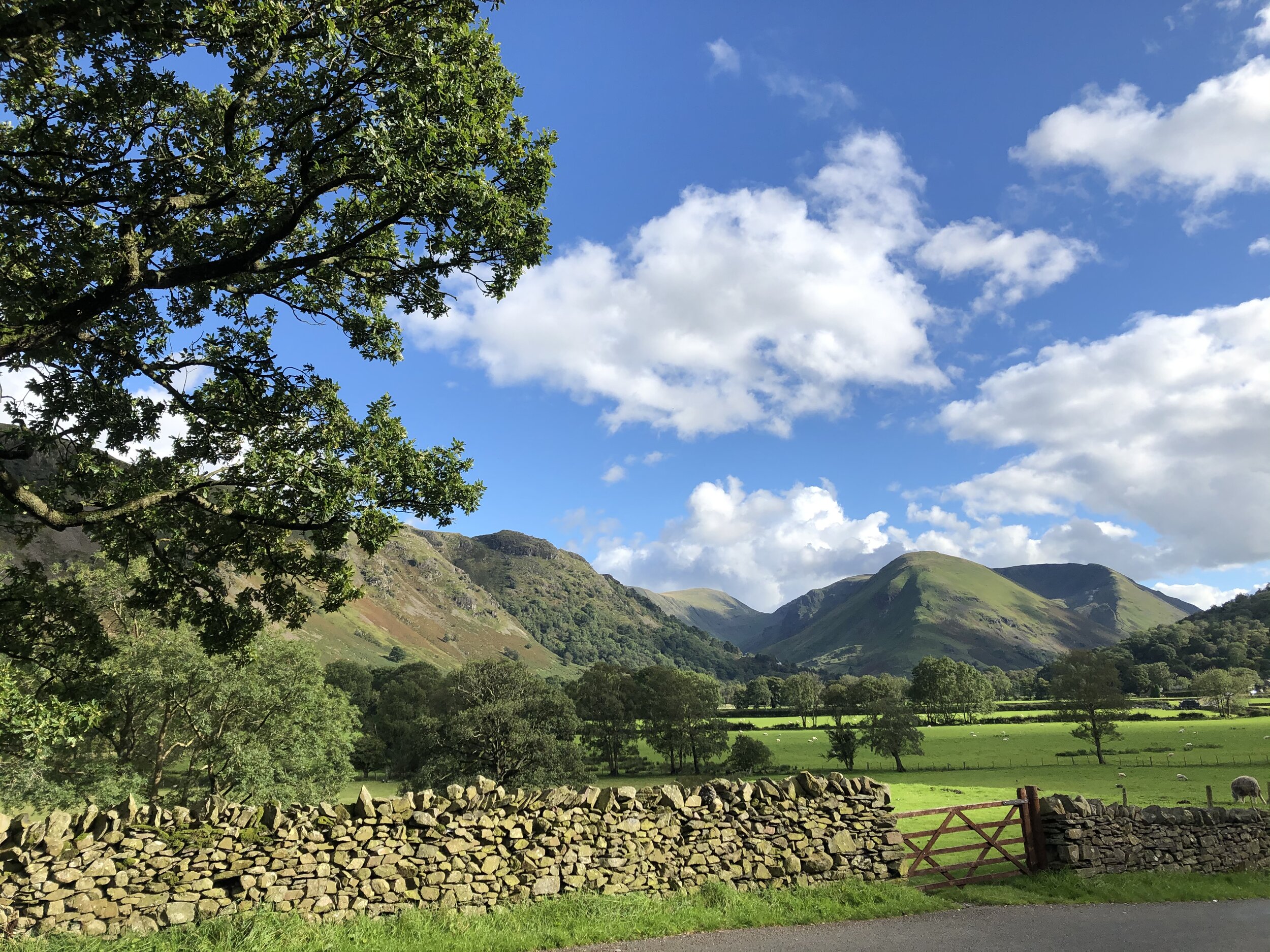

The lush green valley on the way into Ullswater, where we’ll be enjoying a rest day.
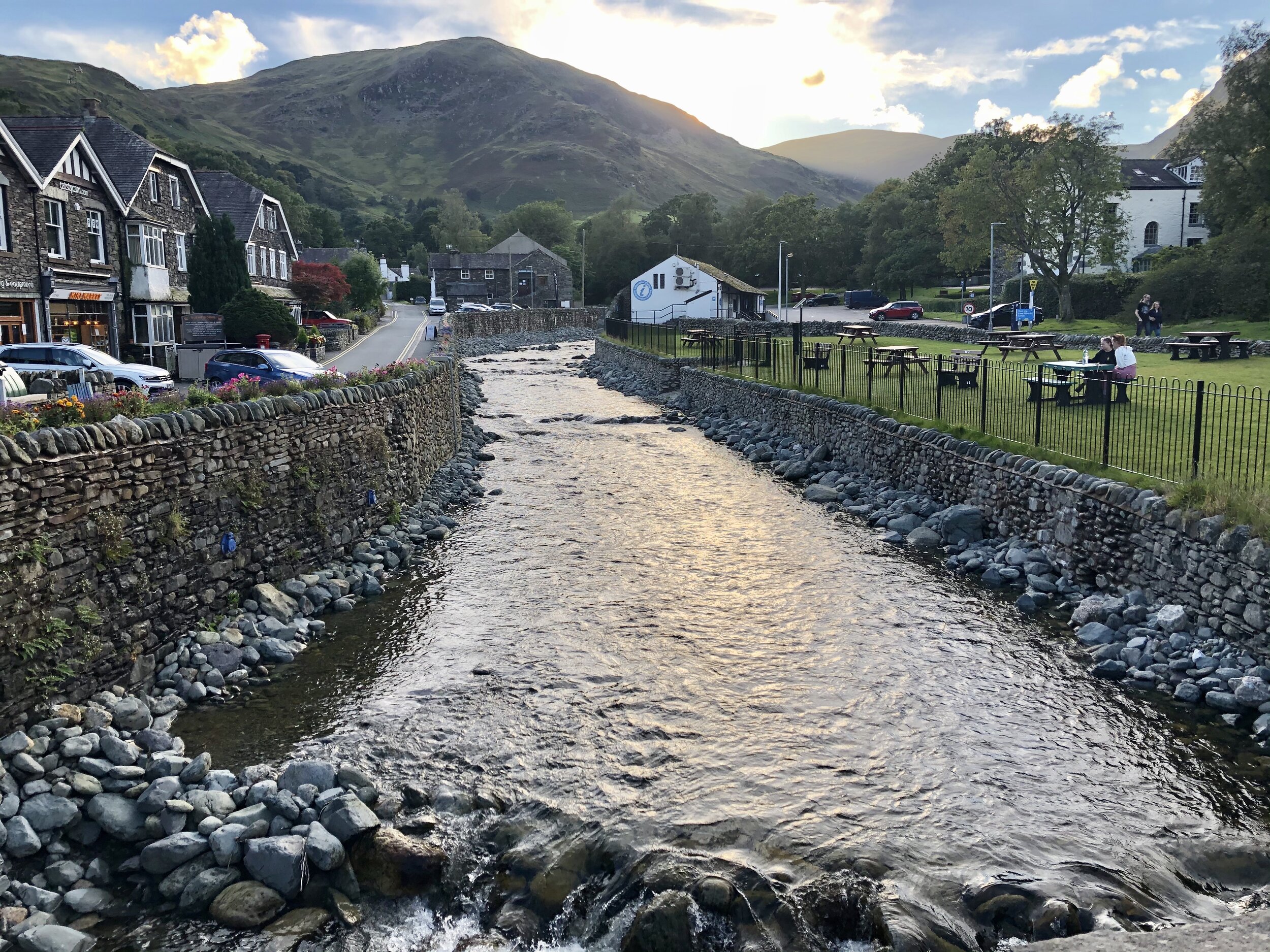

Sat outside the pub, surrounded by mountains as the sun sets and we enjoy burger and chips, washed down with beer and wine (only one each of course!).